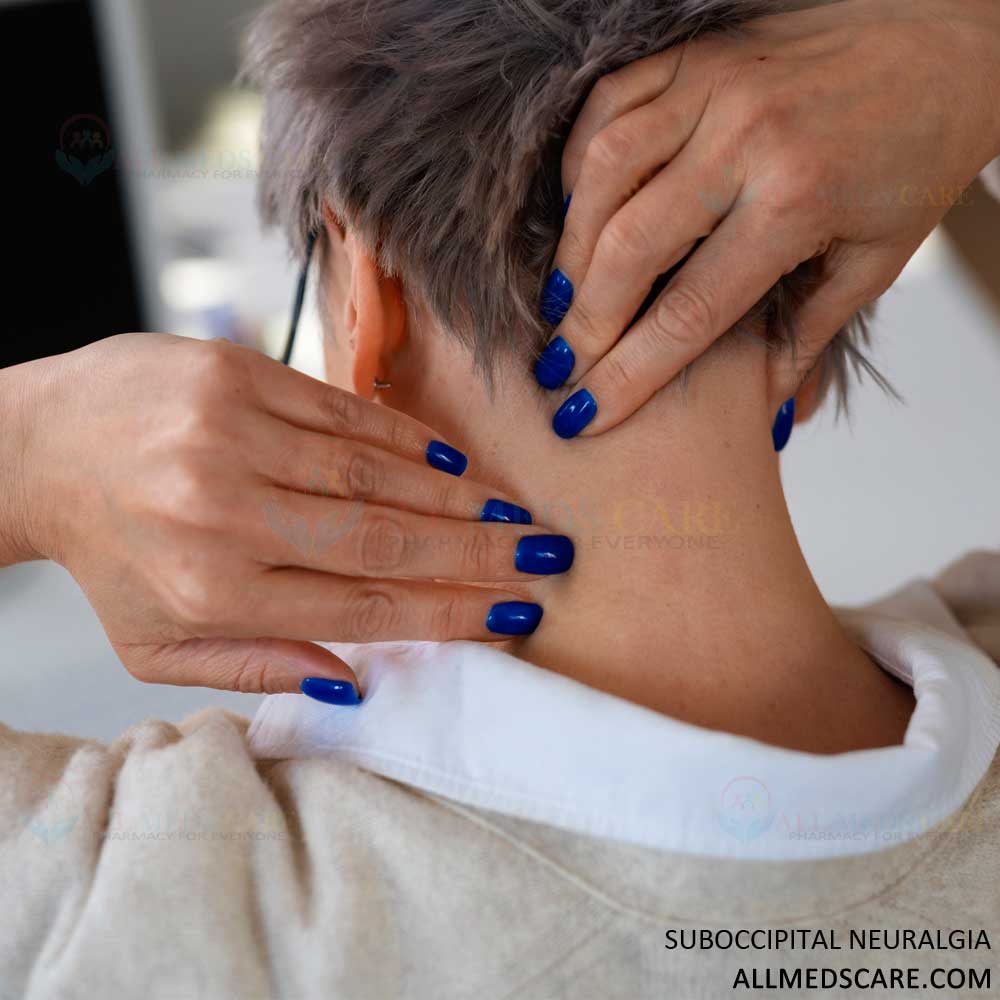
Suboccipital Neuralgia
Do you regularly revel in a pointy, stabbing pain at the base of your cranium? It is probably a sign of suboccipital neuralgia. This lesser-mentioned situation can motivate pain and feature an effect on your daily life if left untreated. In this blog publish, we can discover the symptoms and symptoms of suboccipital neuralgia and what you must look out for to search for the correct remedy. Stay tuned to look at more about the way to become aware of and control this regularly misunderstood condition!
Introduction to Suboccipital Neuralgia
Suboccipital neuralgia is a form of headache that is due to infection or compression of the suboccipital nerves, moreover known as the extra occipital nerves. These nerves originate from the lowest of the cranium and run upwards closer to the scalp, imparting sensation to the decrease once more of the top, neck, and within the once more of the eyes.
This circumstance can be especially debilitating for folks that are through it. The ache can range from moderate soreness to immoderate throbbing sensations that might last for days. It commonly impacts one aspect of the pinnacle however in some times, it may moreover have an effect on each element.
What Are Suboccipital Neuralgia Symptoms?
Submandibular neuralgia is an illness that impacts the nerves within the upper neck and return of the pinnacle, additionally known as the submandibular place As with any neurological situation, signs and symptoms can range from person to man or woman. In this segment, we will dive into the maximum commonplace signs related to Suboccipital Neuralgia and the way it could have an effect on each day’s lifestyles.
The maximum outstanding symptom of Suboccipital Neuralgia is a pointy or capturing pain in the lower back of the top or below the skull. This ache can radiate to different regions as nicely, including at the back of the eyes, hips, or forehead. The depth of the ache varies from slight to severe and can be described as throbbing or burning. It can also stand up intermittently or close for days at a time. Perhaps reading an article on treating back pain can be helpful.
Another commonplace symptom of suboccipital neuralgia is neck stiffness and lack of motion. Due to infection of the sufferer’s spinal twine, patients may additionally experience muscle stiffness and stiffness in the neck that makes it tough for them to show their head or appearance up and down. This stiffness can motivate dizziness itching and further anxiety the ache within the affected vicinity.
In addition to bodily symptoms, people with Suboccipital Neuralgia may revel in sensory problems which includes numbness or numbness within the scalp, neck, ears or maybe the face This is due to compressed nerve pathways blocking signals among your Among the brain and body.
In some cases, patients may experience psychological issues such as difficulty concentrating, memory loss, or mental fog. These symptoms are caused by chronic pain that disrupts normal brain function often leading to fatigue-like symptoms.
Additionally, patients with Suboccipital Neuralgia may report sensitivity to light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia). These stimuli can exacerbate pain and cause discomfort even when performing simple daily tasks.
Understanding these specific types of physiological responses in the context of stimulation is important for the diagnosis of suboccipital neuralgia. Keeping a journal and recording the severity, duration, and chronology of these symptoms can help physicians make a more accurate diagnosis.
It should be noted that although these are the most commonly reported symptoms, everyone’s experience with Suboccipital Neuralgia can vary with some patients experiencing one or both of these symptoms, when due that others deal with several at once.
Finding the real cause of your problem starts with paying close attention to your body’s signals. Knowing the most common symptoms of suboccipital neuralgia can bring understanding and relief to individuals seeking diagnosis, treatment and a life free of pain interference.
Causes of Suboccipital neuralgia
There are many possible reasons for Suboccipital neuralgia, starting from bodily injury to underlying medical conditions. Understanding these causes can help someone better understand symptoms and are trying to find appropriate treatment.
- Injury: One of the maximum not unusual reasons of sub-neck is harm or trauma to the head and/or neck. This can consist of whiplash from car injuries, sports activities injuries, falls, and even minor bumps or strains. These accidents harm the sub capillary part of the tissue, inflicting irritation and pain.
- Poor posture: Many human beings spend lengthy hours sitting at a table or bent over digital devices, leading to negative posture and neck muscle stiffness. Over time this has positioned strain on the muscle tissues within the sub capillary area and it can cause swelling.
- Arthritis: As we age, we can broaden damage to our joints known as arthritis. When this impacts the joints of the higher backbone (cervical backbone), it causes compression of the subclavian nerve and may cause pain.
- Pink muscular tissues: Other arthritis-like issues consisting of spinal hernias (spinal wire accidents) or muscle spasms can also compress muscle mass in the cervical spine to assist set off the muscular tissues inside the decreased lower back.
Identifying these danger factors for sub-capillary neuralgia can assist individuals understand their danger elements and, if essential, seek preventive measures. By addressing the underlying issues or seeking appropriate treatment for the harm, one could normally locate relief from this distressing situation.
General symptoms of Suboccipital neuralgia
It can cause excessive pain and soreness inside the neck and in the upper shoulder. Such pain is regularly described as sharp or stabbing, and can be debilitating to those who suffer from it. In this section, we will discuss a number of the commonplace signs related to sub capillary neuralgia.
- Headache: One of the hallmarks of sub capillary neuralgia is steady headache. This form of headache is normally based behind the top and may spread to other areas along with the jaw or brow. Mild to severe ache can remain for hours or even days.
- Neck pain: Many people with neck ache additionally revel in neck pain. This ache is usually positioned at the base of the skull and causes stiffness or immobility inside the neck. Some sufferers also document a feeling of tightness or tightness within the neck muscle groups.
- Shoulder ache: In a few instances, sufferers with subdural neuralgia may additionally experience shoulder pain. This may be due to transferred pain from nerves strolling in this region as they keep to offer sensation to the lower back of the head.
- Tingling sensation: Sub-capital neuralgia also can cause numbness in certain regions of the head, including in the back of one ear or on top of the cranium This sensation comes and goes but is extra not unusual when you are experiencing sub- capital neuralgia flashes .
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Suboccipital Neuralgia
Sub-capital neuralgia may be difficult to diagnose, as its signs can overlap with those of different headache sorts. However, there are processes and approaches by means of which healthcare professionals should diagnose subchondral neuralgia. Once recognized, treatments are available to assist control symptoms and enhance standard top notch of life.
Diagnosis:
- Physical Exam: During your bodily exam, your scientific doctor will assessment your medical records and perform an entire head and neck exam. They can also check for loosening or tightening of the muscle mass particularly areas close to the lowest of the cranium.
- Neurological examination: Neurological exam includes assessment of neurological signs, motor abilities, sensation, and muscle power.
- Imaging tests: Your doctor may order imaging assessments together with an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT scan (computed tomography) to rule out any causes, such as spinal compression or nerves harm or tissue harm .
- Blocked nerves: In some instances, diagnostic nerve blocks can be used to understand the nerves that are causing the ache. In this approach, anaesthesia is injected into specific tissues to quickly numb them. Relief of pain after massage shows that that precise nerve is concerned in sub capillary neuralgia.
Treatment:
- Neck massage: Massaging subcarinal muscular tissues can help relieve tension and decrease pain in masses of instances.
- Exercise: Targeted wearing occasions and stretches prescribed by a physical therapist can improve posture and decorate neck muscular tissues and offer relief from pain within the situation.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory capsules (NSAIDs), acetaminophen or muscle relaxants or steroids may be prescribed in keeping with personal goals.
- Nerve blocks: Nerve blocks now not handiest have a diagnostic reason but can also offer lengthy-term ache consolation. Antibiotics used in injections can intervene with pain indicators and suppress infection.
- Botox injections: In a few times, Botox injections may be recommended to loosen up muscle spasms and reduce pain.
- Nerve Stimulation Techniques: Techniques which incorporate transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS) or posterior pituitary nerve stimulation use electric impulses to block ache alerts and provide alleviation.
In addition to remedy, manner of life changes in conjunction with preserving a healthy posture, coping with stress degrees, and warding off stimuli such as excessive show display time can help manipulate sub skeletal muscle ailment symptom management.
Importantly, not all remedy alternatives paintings for everyone. Some may additionally want a combination of remedies to get excellent outcomes. Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial so one can create an individualised remedy plan tailor-made on your specific wishes.
The prognosis of sub capillary neuralgia involves a radical exam by using a healthcare professional, and appropriate imaging studies if essential. There are remedy options to be had counting on the severity of the ache and the cause of the collision.






