- Sildenafil Citrate
-
Kamagra $56.00 – $236.00
-
Malegra 100mg $49.00 – $213.00
-
Suhagra 100mg
Rated 4.77 out of 5$38.00 – $164.00 -
Caverta 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$160.00 – $720.00 -
Fildena 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$49.00 – $212.00
-
- Tadalafil
-
Tadalis Soft Gel Capsule 20mg $56.00 – $215.00
-
Vidalista 20mg $46.00 – $192.00
-
Tadaga 40mg $68.00 – $249.00
-
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Tadalis 20mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$65.00 – $182.00
-
- Vardenafil
-
Snovitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$67.00 – $234.00 -
Vilitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$68.00 – $165.00
-
- Dapoxetine
-
Super Kamagra 160mg
Rated 4.83 out of 5$124.00 – $455.00 -
Prejac 60mg
Rated 4.67 out of 5$56.00 – $125.00 -
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Super P-Force 160mg $73.00 – $250.00
-
Although ophthalmology and optometry both deal with eye care, there are differences between them in terms of their practice areas, levels of education, and the services they provide. We shall examine the main distinctions between ophthalmology and optometry in this essay.
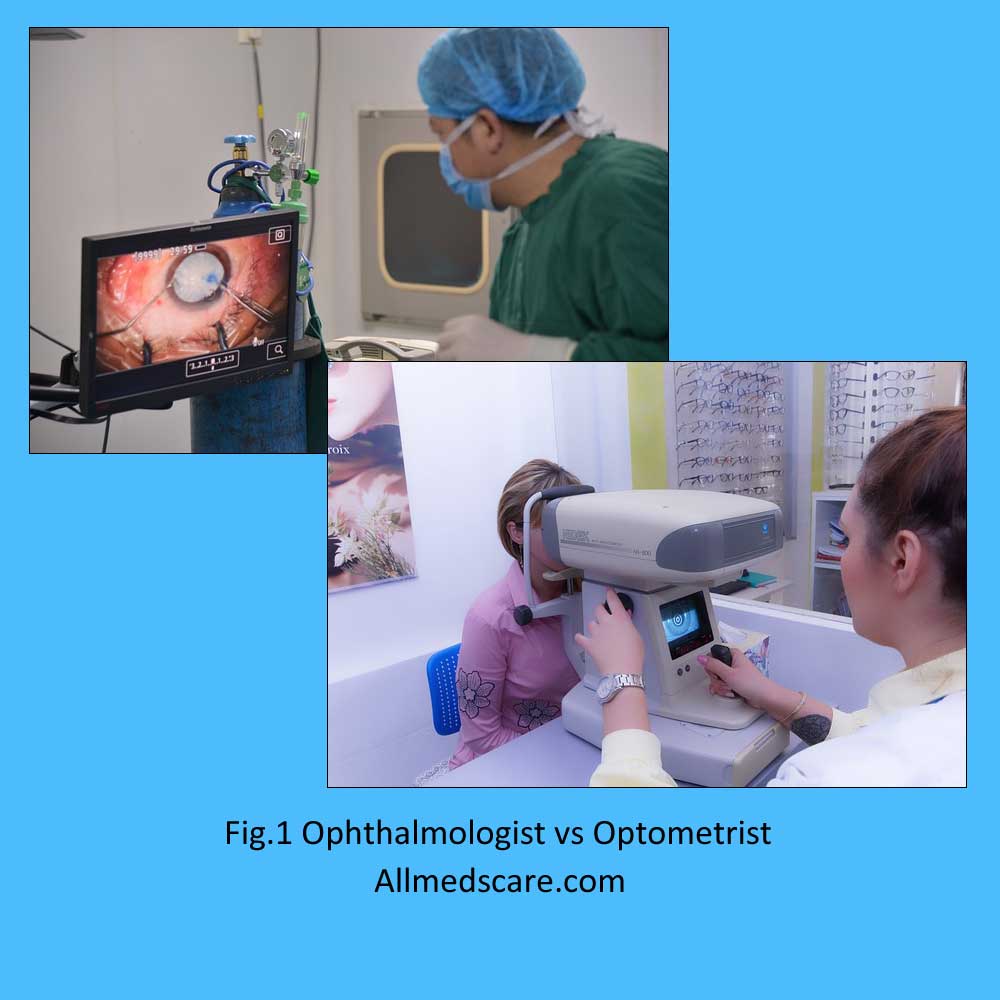
Optometry
Optometrists are medical practitioners that focus on identifying and treating eye and vision conditions. They have received training in prescribing eyeglasses, contacts, and low-vision devices, and offering vision treatment. A number of eye disorders, such as glaucoma, cataracts, and diabetic retinopathy, are also diagnosed and treated by them.
A four-year Doctor of Optometry (OD) degree program from an authorized optometry institution is required to become an optometrist. Topics including optics, physiology, pharmacology, and ocular anatomy are all covered in this program. A set of tests must also be passed by optometrists before they can obtain a license to work in their state or nation.
However, they may also work in hospitals or other healthcare facilities. Optometrists typically have their own private practices. They might work together with eye doctors and other medical personnel to manage complex eye conditions.
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmologists are medical professionals with a focus on the identification and management of eye disorders and diseases. They have received training in performing surgeries on the eyes, such as LASIK, corneal transplants, and cataract surgery. They can also identify and treat a wide range of eye problems, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and retinal detachment.
One must complete four years of medical school, a one-year internship, and a three-year residency in ophthalmology before becoming an ophthalmologist. Ophthalmologists undergo specialized training in surgical methods and medical therapy for eye problems during their residency.
Additionally, ophthalmologists have the option of completing additional subspecialty training in fields like pediatric ophthalmology, retina, or glaucoma. In order to obtain a license to practice medicine in their nation, they must also pass a set of tests.
Ophthalmologists often work in hospitals, private practices, or other healthcare settings. Additionally, they might carry out research and instruct medical students and residents in academic settings.
Differences between Ophthalmology and Optometry
Practise Area
The primary distinction between optometry and ophthalmology in their respective areas of specialization. While ophthalmologists are trained to perform surgical procedures and manage more complicated eye conditions, optometrists concentrate on the diagnosis and non-surgical treatment of vision issues and eye diseases.
Training associated with Ophthalmology and Optometry
The education needed to become an ophthalmologist differs from that needed to become an optometrist. While ophthalmologists must complete four years of medical school, followed by a one-year internship and a three-year residency in ophthalmology, optometrists complete a four-year Doctor of Optometry (OD) program.
Services Offered in Ophthalmology and Optometry
Optometrists and ophthalmologists provide different services. Doctors of optometry are qualified to recommend eyeglasses, contact lenses, low-vision devices, and vision treatment. A number of eye disorders, such as glaucoma, cataracts, and diabetic retinopathy, may also be diagnosed and treated by them.
On the other hand, ophthalmologists are qualified to carry out surgeries on the eyes, such as cataract surgery, LASIK, and corneal transplants. They can also identify and treat a wide range of eye problems, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and retinal detachment.
Referral Procedure
An optometrist may need to recommend a patient to an ophthalmologist in various circumstances in order to receive additional testing or treatment. This usually happens when the patient needs surgical treatment for a more severe eye disease.