- Sildenafil Citrate
-
Kamagra $56.00 – $236.00
-
Malegra 100mg $49.00 – $213.00
-
Suhagra 100mg
Rated 4.77 out of 5$38.00 – $164.00 -
Caverta 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$160.00 – $720.00 -
Fildena 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$49.00 – $212.00
-
- Tadalafil
-
Tadalis Soft Gel Capsule 20mg $56.00 – $215.00
-
Vidalista 20mg $46.00 – $192.00
-
Tadaga 40mg $68.00 – $249.00
-
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Tadalis 20mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$65.00 – $182.00
-
- Vardenafil
-
Snovitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$67.00 – $234.00 -
Vilitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$68.00 – $165.00
-
- Dapoxetine
-
Super Kamagra 160mg
Rated 4.83 out of 5$124.00 – $455.00 -
Prejac 60mg
Rated 4.67 out of 5$56.00 – $125.00 -
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Super P-Force 160mg $73.00 – $250.00
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic health condition that affects the digestive system such as the colon and small intestine. A complicated disease with a range of symptoms, causes, and a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. In this blog, we are going to discuss the different types of IBD, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Different Types of IBD
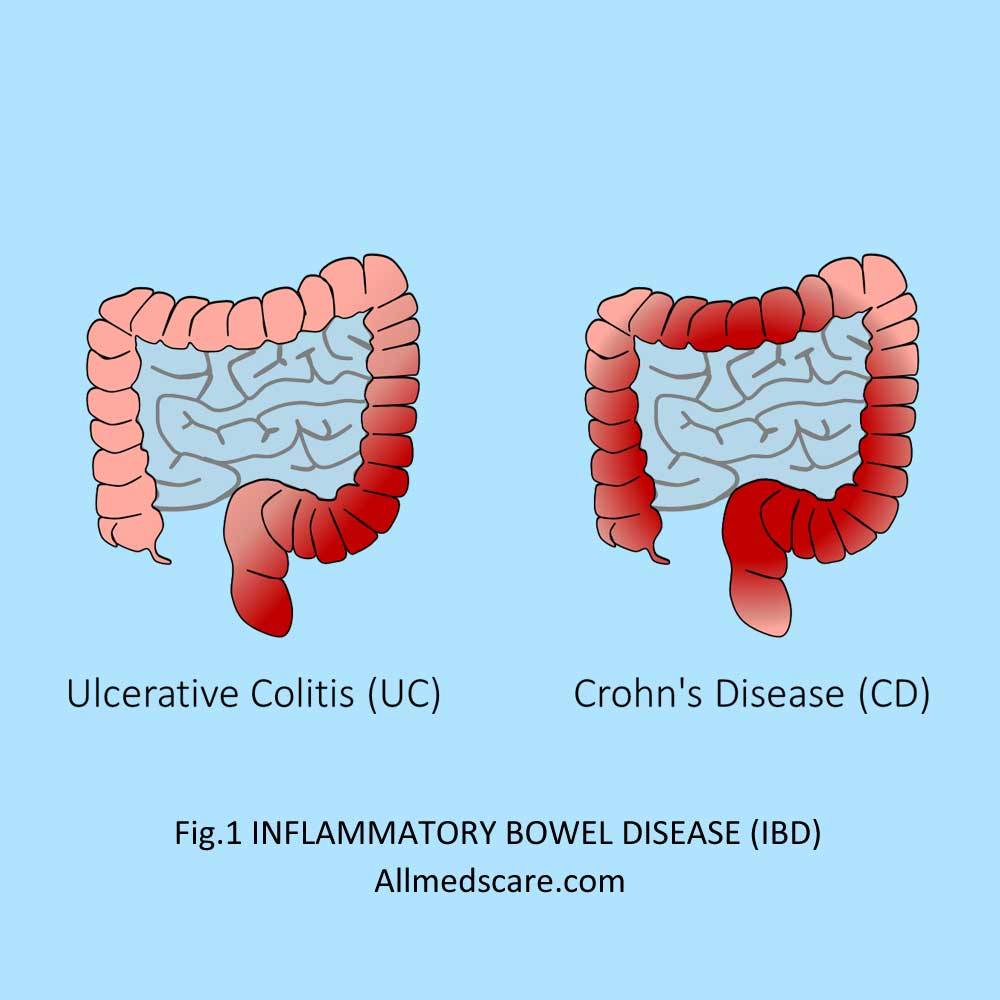
Here are two different types of IBD including Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn’s Disease. Both diseases have similar conditions but they have different parts of the digestive tract.
1. Ulcerative Colitis
lcerative Colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that initially affects the large intestine which is the colon and rectum. The condition causes inflammation and ulcers to form in the lining of the colon, which leads to the symptoms such as abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and diarrhea.
The exact causes of ulcerative colitis are not understood, but it seems to be an autoimmune disorder in that the immune system of the body attacks the lining of the colon and causes inflammation. Some of the factors such as environmental triggers, genetic factors, and lifestyle factors such as stress, and diet can also play an important role to develop Ulcerative Colitis.
Ulcerative colitis may affect any age group of people, but most of the time it is commonly happen in the range of 15-30 years of age people and also found in the age range between 50-70 years. It is more extensive in developed countries.
Let’s discuss the symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis. It varies as per the severity of the person and includes diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, rectal bleeding, weight loss, and urgency to have a bowel movement. These symptoms may occur for a few times and disappear, but some people can experience these symptoms for a long period of remission.
Right now, there is no cure for Ulcerative Colitis, but have different types of treatments available that can help to reduce the inflammation in the colon and symptoms. Some treatment options such as medications include anti-inflammatory drugs, biologic therapies, and immune system suppressors. In some extreme cases, surgery is needed to remove the affected area of the colon.
2. Crohn’s disease
Crohn’s disease is another type of IBD that can affect any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus. But mostly it affects the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine.
Cause of Crohn’s Disease:
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown but the researcher may conclude that an autoimmune reaction can be one of the causes attack the lining of the digestive tract and damage the healthy cells in your body. Crohn’s disease may occur because of environmental factors such as smoking, alcoholism, and certain foods.
People with Crohn’s disease may experience severe symptoms followed by periods of no or very mild symptoms. if you have Crohn’s disease then you might experience symptoms such as Abdominal pain, Chronic diarrhea, A feeling of fullness, Fever, A loss of your appetite, Weight loss, Abnormal skin tags, Anal fissures, Anal fistulas, and Rectal bleeding.
Diagnosis of Crohn’s disease generally involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, medical history, stool tests, and imaging tests like a CT scan or colonoscopy. A biopsy is also effective to diagnose Crohn’s disease.
Treatments for Crohn’s disease are a combination of a healthy lifestyle and medications. Some of the medications include anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, biological therapies, and immunosuppressants. Healthy lifestyles such as stress management, diet modifications, and regular exercise.
Living with Crohn’s disease may be challenging if you are not doing anything, but if you go with proper treatment and management the disease are able to lead full and active lives. A person with Crohn’s disease may consult with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment of IBD(Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
There are several treatments available that can help to improve the quality of life and manage symptoms.
Medications: Corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics are just a few of the drugs that help lessen inflammation in the digestive tract. Medication schedule is recommended by the doctor based on circumstances.
Surgery: To remove the damaged area of the digestive tract in severe cases of UC or Crohn’s disease, surgery may be required.
Lifestyle Changes: Changes in lifestyle can help manage symptoms and enhance the quality of life. These include eating a balanced diet, staying away from trigger foods, and lowering stress.
Alternative treatments: Acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements are a few examples of alternative treatments that some people with IBD find helpful. Before attempting any alternative therapies, it’s crucial to speak with your doctor because they can interact with your prescription drugs.