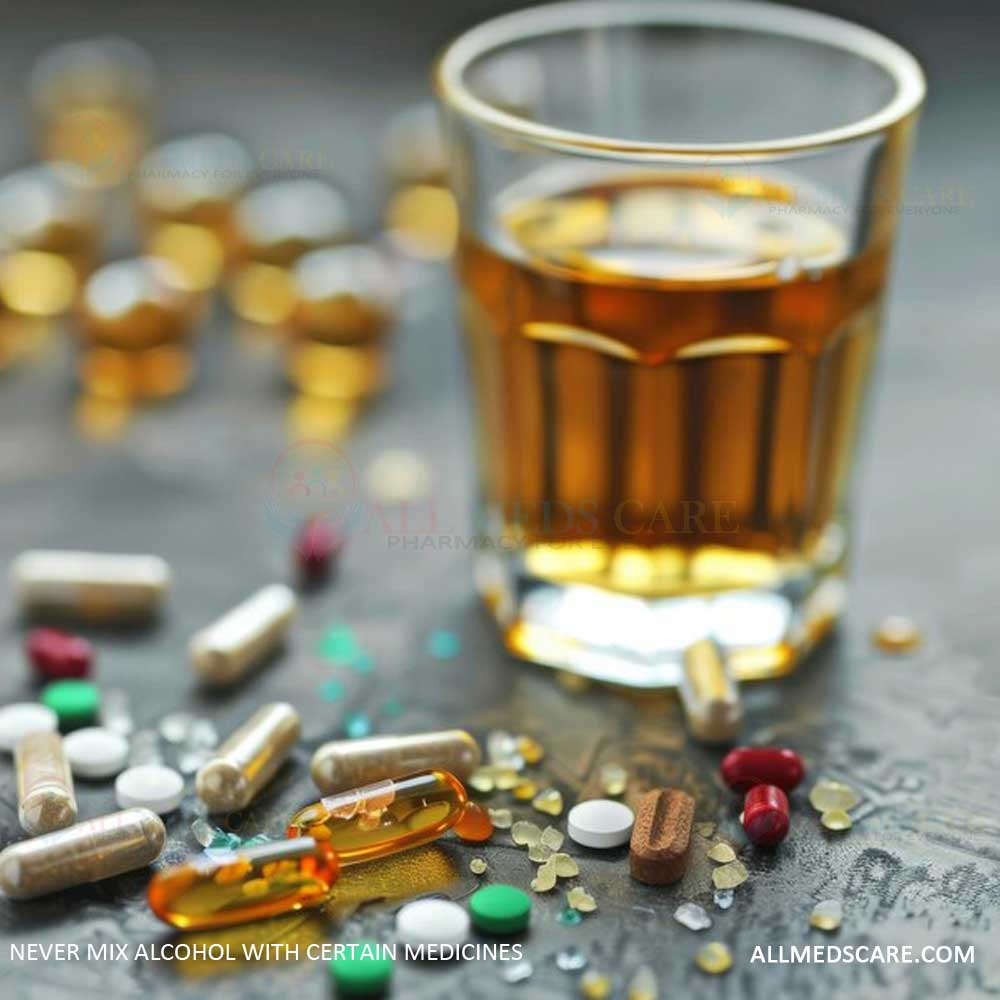
Never Mix Alcohol with Certain Medicines
Never mix alcohol with certain medications because this can lead to serious and potentially fatal consequences. While many people know about the general dangers of combining alcohol and drugs, the specific interactions between them are often overlooked or taken too lightly.
Alcohol and drugs can interact and change how each affects the body, leading to more side effects, poor judgment, and increased chances of accidents or overdoses. These interactions can happen with prescription and over-the-counter medicines, as well as some herbal products.
This guide aims to inform people about the risks of mixing it with various drugs. By knowing which drugs to avoid with alcohol, individuals can better protect their health. It’s essential to prioritize safety and talk openly with healthcare providers to prevent dangerous situations.
How Alcohol Interacts with Medications?
- Alcohol can significantly affect the way drugs work in the body, leading to potential adverse effects and health risks. Interactions between alcohol and drugs occur due to various pharmacological mechanisms and metabolic changes.
- Alcohol can interfere with the absorption, distribution, and metabolism of certain drugs. When consumed together.
- It can either increase or decrease the concentration of a drug in the bloodstream.
- Enzymes in the liver metabolize alcohol and drugs. When consumed together, they can compete for these enzymes, leading to slower or faster breakdown of foods.
- Mixing alcohol and drugs can stress the liver, kidneys, and other organs responsible for metabolizing and eliminating these substances from the body.
Common Medications That Shouldn’t Be Mixed with Alcohol
Mixing it with certain medications can lead to dangerous and even life-threatening consequences. Here are some common medications that should never be combined with alcohol:
Antibiotics
Combining antibiotics with alcohol is not recommended. Because mixing antibiotics with it can cause serious side effects reduce the effectiveness of the medicine and can also have adverse effects on the body. Alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for antibiotics to effectively fight infections. It can also increase the side effects of some antibiotics, including dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, and stomach upset. This can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, which can be especially harmful to individuals with underlying health conditions.
Alcohol can interfere with the absorption and metabolism of certain antibiotics, reducing drug concentrations in the bloodstream. This can reduce the ability of antibiotics to effectively fight infection, prolong illness, and cause bacteria to develop resistance.
Some specific antibiotics that should not be mixed with alcohol include:
- Metronidazole (Flagyl): Combining metronidazole with alcohol can cause severe nausea, vomiting, flushing, and a rapid heart rate.
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim): It can increase the risk of side effects like dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion when taken with this antibiotic.
- Isoniazid (INH): Used to treat tuberculosis, isoniazid can interact with alcohol, potentially causing liver damage.
It is important to follow the instructions given by healthcare professionals and to read medication labels carefully. If you are prescribed antibiotics, it is usually advised to avoid it until you finish the treatment and the infection is completely cleared.
Pain Medications
It can be exceedingly harmful and even fatal to combine it with painkillers, such as opioids (oxycodone, hydrocodone) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as naproxen and ibuprofen). Alcohol and these drugs depress the central nervous system in the same way, which causes drowsiness, sluggish breathing, and decreased coordination.
Alcohol can greatly intensify the sedative effects of opioid medications, raising the possibility of respiratory depression, coma, and even death. The drowsiness and dizziness brought on by opioids can be exacerbated by even moderate use, which makes tasks like operating machinery or driving exceedingly dangerous.
NSAIDs combined with alcohol can irritate the stomach lining and raise the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Regularly using alcohol and NSAIDs together can result in ulcers, internal bleeding, and liver damage.
Antidepressants
Mixing antidepressants with it can be harmful and have serious repercussions. Antidepressants are prescription drugs used to treat anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. They function by changing the brain’s concentrations of specific neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
Some specific interactions between antidepressants and alcohol include:
- Increased Risk of Overdose: It can intensify the effects of some antidepressants, raising the risk of a dangerous overdose.
- Increased Side Effects: The combination of antidepressants and alcohol can exacerbate side effects such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and impaired coordination.
- Liver Damage: Both antidepressants and alcohol can strain the liver, and their combined use increases the risk of liver damage or liver failure.
- Worsening of Depression and Anxiety: It is a depressant that can make depression and anxiety worse and can interfere with antidepressants.
Blood Thinners
Combining blood thinners (anticoagulants can be a dangerous combination. Blood thinners, such as warfarin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban, are prescribed to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of stroke or heart attack. However, when used in combination, these drugs can increase the risk of heavy bleeding.
Additionally, It can interfere with the metabolism and effectiveness of blood thinners, leading to unpredictable levels of the drug in the bloodstream. This can either reduce the drug’s ability to prevent clots or increase the risk of heavy bleeding.
Erectile Dysfunction Medicines
It is usually not advised to take it in addition to erectile dysfunction (ED)drugs like Cenforce, Kamagra, Aurogra. When these drugs are combined , there is an increased chance of adverse effects such as dizziness, and fainting. Alcohol and ED medications both have the potential to cause a hazardous reduction in blood pressure. To reduce hazards and maintain treatment effectiveness, it is essential to abstain from excessive use when using Erectile Dysfunction drugs. See a doctor for specific guidance on controlling it use with ED drugs.
Diabetes Medications
Alcohol and diabetes drugs together can result in hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. Because it prevents the liver from making glucose, drinking it together with some diabetic treatments can significantly lower blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia is a dangerous illness that, particularly in diabetics, can result in seizures or loss of consciousness. Blood sugar levels should be closely watched when taking diabetic medicines together.
Furthermore, alcohol and several diabetic drugs may interact negatively, and the risk of certain side effects, like flushing, nausea, and dizziness. It is essential to discuss your medication regimen and any potential interactions with alcohol with your healthcare professional to guarantee optimal outcomes.
Recognizing the potential drug Interactions
Being aware of the potential signs and symptoms of adverse interactions with medications is crucial for your safety and well-being. While the specific effects can vary depending on the substances involved, there are some common indicators to watch out for:
- Dizziness and Impaired Coordination: Alcohol and certain medications can both cause dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired coordination. When combined, these effects can be amplified, increasing the risk of falls, accidents, and injuries.
- Nausea and Vomiting: It use may make certain pharmaceutical side effects worse, such as nausea and vomiting. Frequent vomiting can result in hazardous electrolyte imbalances and dehydration.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Alcohol and some medications can impair thinking and decision-making, causing confusion and disorientation, which is especially worrying in situations needing focus and good judgment.
- Excessive Drowsiness: Many drugs include drowsiness as a common side effect, and combining it with pharmaceuticals can result in excessive sleepiness, which is dangerous while operating machinery or performing duties that need concentration.
- Irregular Heartbeat or Blood Pressure Changes: Alcohol and certain medications can affect the cardiovascular system, potentially leading to irregular heartbeat, high or low blood pressure, or other heart-related issues.
- Respiratory Depression: In severe cases, drinking it together with other drugs, such as sedatives or opioid medicines, can cause respiratory depression. This condition can be fatal if left untreated.
Tips for Safe Medication Use and Alcohol Consumption
To avoid dangerous interactions with medications, it’s essential to follow these practical tips:
- Read Labels Carefully: Before using any medication, read the label and any information about interactions. If there is warning, it is important to follow that advice.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Never hesitate to speak with your healthcare physician if you have questions regarding the safety of combining alcohol use with a certain prescription. Based on your medical history and the particular medications you take, they can offer you tailored advice.
- Avoid Alcohol Entirely: If your medications interact with it, it’s best to avoid drinking. This reduces risks and helps the medication work properly.
- Limit Consumption: If your doctor says it’s safe to drink it in moderation while on certain medications, be sure to limit how much you drink. Moderate drinking is usually up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Time Your Medications and Alcohol Intake: If you drink it while on medication, space out the times you take your medicine and drink. This can help reduce interactions and let your body process both substances separately.
- Stay Hydrated: It can cause dehydration, raising medication levels in your body. Drink water and stay hydrated when drinking it with medications.
- Be Aware of Symptoms: Watch for unusual symptoms after mixing it with medications. If you feel dizziness, nausea, or extreme drowsiness, get medical help right away.
Remember, responsible medication use and alcohol consumption are crucial for maintaining your health and well-being. By following these tips and consulting with healthcare professionals, you can minimize the risks associated with mixing alcohol and medications.