- Sildenafil Citrate
-
Kamagra $56.00 – $236.00
-
Malegra 100mg $49.00 – $213.00
-
Suhagra 100mg
Rated 4.77 out of 5$38.00 – $164.00 -
Caverta 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$160.00 – $720.00 -
Fildena 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$49.00 – $212.00
-
- Tadalafil
-
Tadalis Soft Gel Capsule 20mg $56.00 – $215.00
-
Vidalista 20mg $46.00 – $192.00
-
Tadaga 40mg $68.00 – $249.00
-
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Tadalis 20mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$65.00 – $182.00
-
- Vardenafil
-
Snovitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$67.00 – $234.00 -
Vilitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$68.00 – $165.00
-
- Dapoxetine
-
Super Kamagra 160mg
Rated 4.83 out of 5$124.00 – $455.00 -
Prejac 60mg
Rated 4.67 out of 5$56.00 – $125.00 -
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Super P-Force 160mg $73.00 – $250.00
-
Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure helps in viewing heart’s arteries. Heart catheterization or coronary arteriography is another name of this procedure. It involves inserting a thin, flexible tube known as a catheter into an artery in your arm or groin and then leading it through the blood vessels to your heart. Once there, Doctor injects contrast dye for detailed imaging of the inner lining of these arteries. This reveals any blockages or narrowing that might exist as a result of plaque formation brought on by high blood cholesterol levels. Coronary angiography assists medical professionals in the diagnosis and treatment planning of coronary artery disease (CAD) and other cardiovascular diseases, such as congestive heart failure.
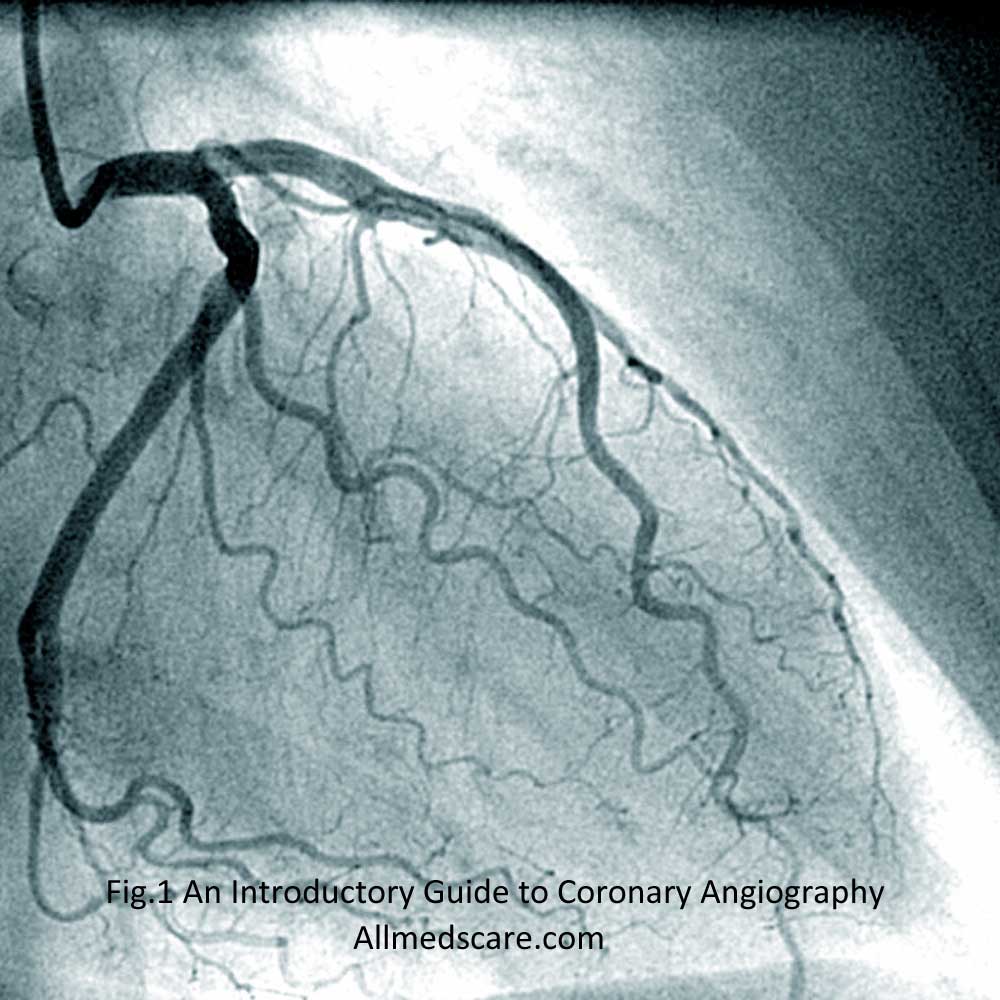
Types of Coronary Angiography
- Computerized Tomographic Angiography (CTA) is helps to view the heart and its blood vessels. To provide accurate three-dimensional images of your arteries, it combines X-ray images taken from various angles. With the use of this imaging technique, doctors may see any blockages or narrowing that may exist in your coronary arteries as well as other cardiovascular-related diseases like valve problems and congenital defects. CTA is a quick procedure that is especially helpful for detecting CAD in patients who are unable to have conventional angiography due to high-risk conditions like kidney illness or major surgery.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) uses magnetic fields rather than X-rays, giving it a safer alternative to conventional techniques. It produces precise images that allow medical professionals to accurately assess the condition of the heart walls and any blockages or narrowing caused by plaque build up on the artery walls. MRA is diagnosis and treatment planning. It takes longer time than other imaging techniques and usually reserved for complex situations when conventional techniques are not suitable.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) uses sound waves rather than X-rays or MRI technology. A long tube called an endoscope and ultrasound probe are inserted into esophagus near your heart. A clear image of any blockages in the blood vessels is created. TEE may take longer than other imaging modalities, but it can offer very accurate information about artery abnormalities that cannot be found with only conventional techniques, making it particularly helpful in the diagnosis of complicated cardiac problems.
Risks and Benefits
- Potential Risks: Coronary angiography is a generally safe treatment, but there are a few potential risks you should be aware of before having the test. These include catheter-related infections, allergic reactions to the contrast dye used during imaging, and blood vessel damage brought on by the catheter itself. In a few rare examples, issues like a heart attack or stroke can happen as a result of artery blockages that are invisible on X-ray pictures.
- Benefits of Coronary Angiography: Despite these risks, coronary angiography has many benefits for patients with cardiac diseases including congestive heart failure or CAD. Doctors are better able to diagnose and plan treatments since it gives them detailed information about what’s happening inside your heart. Balloon angioplasty or stenting help to remove arteries blockages or narrowing’s using this type of imaging. Furthermore, coronary angiography is a crucial technique for determining whether bypass surgery is necessary for some patients who are not suitable candidates for other treatment choices like medication alone.
Preparing for the Exam
- Pre-Exam Questions: Your doctor will inquire about your medical history and present health condition before doing coronary angiography safely and without complications. Before doing the surgery, they could also ask for specific tests like blood work or an electrocardiogram (ECG) to better understand any potential underlying issues you might have.
- Fasting & Medications: Before having coronary angiography, your doctor will probably advise you not to eat or drink anything for at least six hours to make the procedure easier for them to perform and to get more accurate imaging results. Additionally, if you take any medications, your doctor will also advise on when to take them before the test because some medications might affect the results of imaging tests or raise the risks of the treatment itself.
- Clothing/Shoes: You must wear comfortable clothing on the day of your appointment and without any metal accents, such as zips or buttons, as they could obstruct the X-ray pictures during the test. Additionally, it is advised not to wear jewelry, especially around the neck where a catheter needs to be inserted for coronary angiography procedures. Also, you should remove all of your footwear before entering the exam room as this can again affect the quality of the images obtained during the exam.
- Transportation: Transportation preparations is important in advance depending on the type of facility performing coronary angiography, either through public transportation services or through private taxis, depending on how far you live and how long it will take you to travel there by car, etc. Some patients may require assistance to get around due to their pre-existing medical conditions so please keep this in mind when making travel arrangements.
The procedure of the Exam
The doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into an artery in your arm or groin in to heart via blood vessels. Once there, The doctor uses contrast dye to enable precise images of arteries. This helps in identifying any obstructions or constrictions brought on by the plaque build-up as a result of high blood cholesterol levels. The procedure usually takes between 30 minutes to an hour depending on several factors such as additional tests and time taken for pictures to get clear results. A relaxing period of 45 minutes before discharge is a normal practice. Some patients may have to stay longer if there were issues with their exam.
Conclusion
In conclusion, coronary angiography is an important procedure for identifying and managing heart-related conditions. It determines artery blockages that could increase the risk of having a heart attack or stroke. Additionally, it can can direct procedures like bypass surgery or stenting. Ultimately, this procedure provides invaluable information that can greatly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.