- Sildenafil Citrate
-
Kamagra $56.00 – $236.00
-
Malegra 100mg $49.00 – $213.00
-
Suhagra 100mg
Rated 4.77 out of 5$38.00 – $164.00 -
Caverta 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$160.00 – $720.00 -
Fildena 100mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$49.00 – $212.00
-
- Tadalafil
-
Tadalis Soft Gel Capsule 20mg $56.00 – $215.00
-
Vidalista 20mg $46.00 – $192.00
-
Tadaga 40mg $68.00 – $249.00
-
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Tadalis 20mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5$65.00 – $182.00
-
- Vardenafil
-
Snovitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$67.00 – $234.00 -
Vilitra 20mg
Rated 4.00 out of 5$68.00 – $165.00
-
- Dapoxetine
-
Super Kamagra 160mg
Rated 4.83 out of 5$124.00 – $455.00 -
Prejac 60mg
Rated 4.67 out of 5$56.00 – $125.00 -
Tadapox 80mg $67.00 – $264.00
-
Super P-Force 160mg $73.00 – $250.00
-
Healthy Arteries and veins are crucial factors in our circulatory system that carries oxygen-rich blood in the different part of the body and return oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart and lungs. The risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases can be considerably decreased by maintaining healthy arteries and veins.
How Arteries Can Become Clogged?
Arteries may become damaged through a process called atherosclerosis which creates plaque on the inner walls of arteries. Plaque is by various substances such as fat, cholesterol, calcium, and cellular waste products. Plaque can build up and harden over time, constricting the arteries and lowering blood flow.
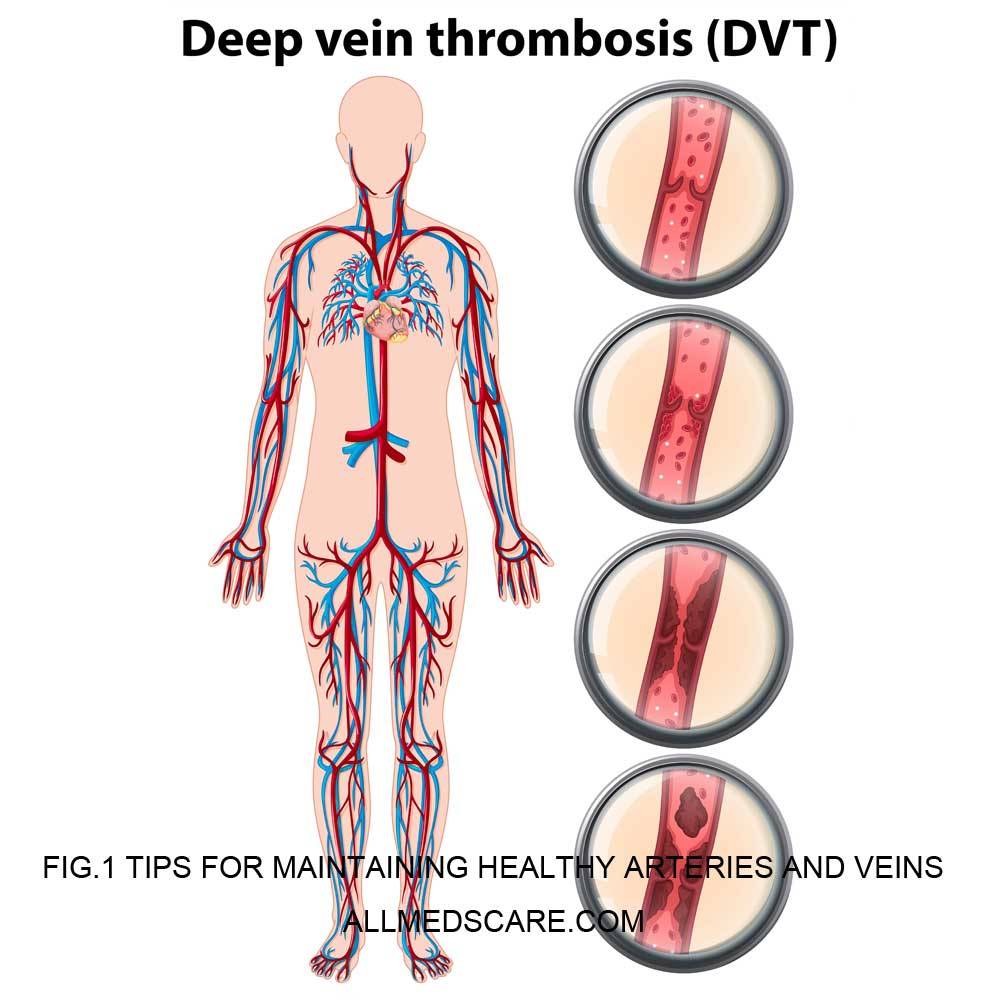
Several factors that hinder Healthy Arteries and Veins:
- High levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol: LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can build up in the artery walls and form plaque. LDL cholesterol levels can be elevated by consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats, smoking, and having a family history of high cholesterol.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the artery walls can lead to the formation of plaque. Inflammation can be caused by various factors, such as smoking, high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels (as seen in diabetes), and infections.
- High blood pressure: Increased pressure on the artery walls can cause damage and create a favorable environment for plaque formation. High blood pressure can result from factors such as an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, stress, and genetic predisposition.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the inner lining of the arteries and increases inflammation, making it easier for plaque to form and progress.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the arteries and contribute to plaque formation.
- Genetics: Family history and genetic predisposition can play a role in the development of clogged arteries. If your parents or close relatives have a history of heart disease or high cholesterol, you may be at a higher risk.
- Lifestyle factors: An unhealthy diet high in saturated and trans fats, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to the formation of plaque in arteries.
Once arteries become clogged, it can lead to various health problems, including reduced blood flow, increased risk of blood clots, and potentially life-threatening conditions such as heart attack and stroke. Therefore, it’s important to adopt a healthy lifestyle, manage risk factors, and seek medical advice for appropriate prevention and treatment strategies.
What are the symptoms of artery damage?
Depending on where and how much damage there is to the arteries, several manifestations of the injury may occur. The following general signs of arterial damage include:
- Pain or discomfort: In the affected location, artery damage may result in pain or discomfort. Pain may be localized or spread to surrounding places, and its severity can range from minor to severe. For instance, artery damage in the heart might result in chest pain (angina), but artery damage in the legs can result in claudication, which is pain or cramping in the legs when moving around.
- Weak or absent pulses: Artery damage can impair blood flow in the artery. This can cause weak or absent pulses in the afflicted location. Depending on where the artery is, you can tell by feeling your pulse at your wrist, neck, groin, or foot.
- Swelling or edema: Artery injury can interfere with regular blood flow, causing swelling or edema in the affected area. Particularly in the legs, feet, or ankles, this may appear as edema or puffiness.
- Skin color or temperature changes: Artery injury can impair the skin’s blood supply, which can result in variations in skin tone or warmth. When touched, the affected area could feel cold and appear pale, blue, or speckled.
Some Other symptoms:
- Numbness or weakness: The numbness of artery reduces blood flow to the nerves. There can be tingling or a “pins and needles” feeling in addition to this.
- Ulcers or sores: In the affected area, especially in the legs or feet, severe artery damage can result in the development of ulcers or sores. These might take longer to heal and come with pain, edema, or infection.
- Changes in organ function: Artery injury that affects the heart’s or brains blood flow can result in symptoms of diminished organ function. Atherosclerosis in the heart, for instance, might result in symptoms like shortness of breath, exhaustion, or dizziness, whereas atherosclerosis in the brain can result in symptoms like weakness on one side of the body, trouble speaking, changes in vision, or problems with coordination.
POINT TO REMEMBER
It’s crucial to remember that artery damage may not always result in obvious symptoms, especially in the beginning. It is important to seek early medical assistance in case of above mentioned symptoms. If you have concerns about the health of your arteries so that you can be properly evaluated, diagnosed, and managed.
Here are the top tips for keeping Healthy Arteries and Veins:
- Eat a Heart Healthy Diet- A balanced diet low in cholesterol, trans fats, and saturated fats will help prevent the artery-clogging formation of plaque and preserve healthy blood flow. a. Eat a heart-healthy diet. Add a lot of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and good fats, such as nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. Also, remember to include lots of other healthy foods.
- Exercise frequently- Cardiovascular health depends on regular physical activity. Aim for 150 minutes or more per week of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling. Exercise lowers the risk of arterial and venous disorders while also enhancing blood flow and strengthening the heart and blood vessels.
- Stop smoking- it increases your risk of developing arterial and venous disorders. It causes damage to the lining of the arteries and veins, which results in plaque build-up and blood vessel narrowing. One of the finest things you can do to improve your venous and arterial health and lower your risk of heart disease is to stop smoking.
- Manage your stress- Arterial and venous disorders might develop due to chronic stress. Find appropriate coping mechanisms for stress, such as meditation, adequate rest, and enjoyment of leisure activities. Maintaining Blood pressure lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Stress management is also important.
- Schedule routine examinations with your healthcare provider- For maintaining and monitoring your venous and arterial health, routine visits to your doctor are crucial. Your medical professional can evaluate your risk factors, monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and offer tailored advice for preserving healthy arteries and veins.























